IMO’s effort to cut GHG emissions from ships
IMO’s effort to cut GHG emissions from ships
IMO adopted various technical and operational measures to reduce GHG emissions from ships.
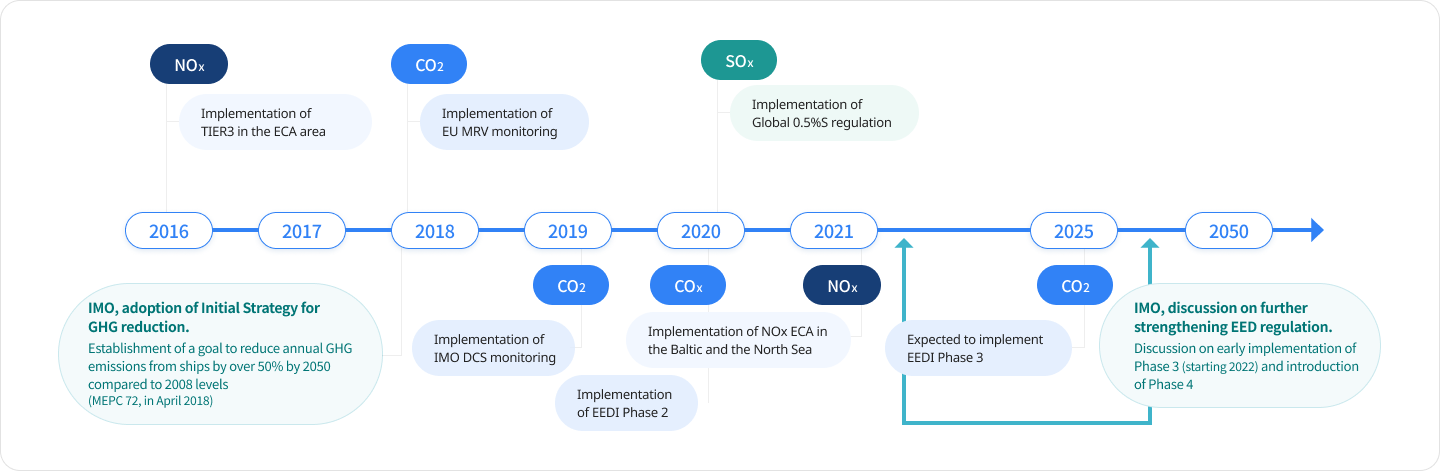
In July 2011, IMO adopted mandatory energy efficiency regulations for ships – Energy Efficiency Design Index (EEDI) for new ships, and Ship Energy Efficiency Management Plan (SEEMP) for all ships by adding a new chapter on "energy efficiency" in MARPOL Annex VI. It is meaningful that GHG emissions from ships begun to be managed in earnest as the regulations entered into force in 2013.
In 2018, IMO adopted IMO Initial Strategy for reducing GHG emissions for achieving decarbonization in the shipping sector. IMO Initial Strategy set a GHG reduction target in international shipping (a 59% reduction by 2050 compared to 2008), and showed its willingness to reduce GHG emissions (at least a 40% reduction by 2030, pursuing efforts towards 70% by 2050, compared to 2008).
In 2023, the IMO adopted the 2023 IMO Strategy on Reduction of GHG Emissions from Ships (IMO GHG Strategy 2023) at the 80th meeting of the Marine Environmental Protection Committee (MEPC), which revised upward the goals of the existing initial strategy. The 2023 Strategy is meaningful in establishing challenging targets and strategies to phase out greenhouse gas emissions by achieving net zero greenhouse gas emissions in the shipping sector by 2050.
The progress of IMO’s GHG reduction
-
20%Until 2030
- Reduce total annual GHG emission from international shipping by at least 20%, striving for 30%
-
70%Until 2040
- Reduce total annual GHG emission from international shipping by at least 70%, striving for 80%
-
100%Until 2050
- Achieving Net-Zero GHG emissions
※ IMO MEPC 80
As amendments to 「MARPOL Annex VI」 were adopted at MEPC 76 in June 2021, IMO's regulations of GHG emission that were only applied to new ships have been expanded to existing ships, and EEXI and CII for existing ships came into effect starting November 2022.
In accordance with CII, ships of 5,000 gross tonnages and above are required to calculate the GHG reduction compared to the annual requirement by collecting ship fuel consumption data and operational data registered in IMO DCS, and ships will be grouped into different CII ratings from A to E, and managed based on the rating.
Standards for GHG emissions and energy efficiency management
| Name | Subject of regulation | Main Contents |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency Design Index (EEDI) | Newbuilding ships | Calculate CO2 emissions per unit of cargo (one ton) and per transportation distance (one nautical mile) during the design process |
| Ship Energy Efficiency Management Plan (SEEMP) | All ships | Detailed plan for ship energy efficiency improvement |
| Energy Efficiency Existing Ship Index (EEXI) | Existing ships | Calculate CO2 emissions per unit of cargo (one ton) and per transportation distance (one nautical mile) in advance, based on the engine output during the operational process |
| Carbon intensity indicator (CII) | Existing ships | Calculate CO2 emissions per unit of cargo (one ton) and per transportation distance (one nautical mile), based on the operational record and fuel consumption, and determine the ship rating from A to E and manage it accordingly |